Patented Wave Energy Technology Gets Its Sea Legs | News
New Technology Could Generate Electricity From Ocean Waves or Even Clothing, Cars,
and Buildings
Imagine this: Clothing that charges your smart watch as you walk, buildings that vibrate
in the wind and power your lights, a road that extracts energy from the friction created
by moving cars, and flexible structures that change shape in ocean waves to generate
clean electricity for communities around the world.
It is not science fiction. Someday, we could harness these naturally occurring energy
sources thanks to a fledgling technology domain that just earned its first patent:
distributed embedded energy converter technologies (or DEEC-Tec, pronounced deck-tech, for short).
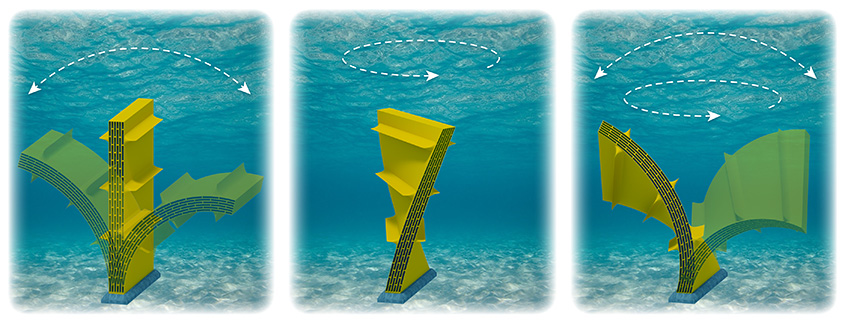
energy converters to create more cost-effective, highly efficient tools for generating
clean energy from the ocean (and beyond). Illustration by Besiki Kazaishvili, NREL
The invention’s first patent is specifically for applications in marine renewable
energy—clean power generated from ocean and river waves, currents, and tides. But
DEEC-Tec could eventually transform sources of everyday energy, including almost all
physical motions or dynamic shape changes, into electricity or other forms of usable
energy.
“The DEEC-Tec domain has legs and is growing,” said Blake Boren, a senior engineer
at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the lead inventor on the patent
along with Jochem Weber, chief engineer for NREL’s water power program. DEEC-Tec might
very well have the legs to move into buildings, clothing, and roads, but it is starting
in the ocean. “The patent shows that we’re gaining momentum in a fruitful area of
research,” Boren said.
So, how does this promising DEEC-Tec domain actually work?
Picture a sea snake. That snake can swim thanks to an intricate partnership between
its many pliable muscle cells. In the DEEC-Tec domain, individual energy converters
work together, like muscle cells, to create a larger structure, much like the sea
snake. Most devices use one generator to convert ocean energy into usable, clean,
and renewable sources of energy, including electricity. But DEEC-Tec amasses its many
tiny converters to form one larger, often flexible energy converter.
“DEEC-Tec gives researchers and developers an entirely new way of thinking about how
to convert marine energy from ocean waves, tides, and currents into more usable forms
of energy, such as electricity,” Boren said.
Combined, these tiny energy converters can form the foundation of fabrics, bulkheads,
support structures, and more, building a range of DEEC-Tec-based energy converting structures. For example, DEEC-Tec-based wave energy converters could look like balloons that
contract and expand, snakes that undulate, or paddles that twist and bend to harness
ocean wave energy.
These adaptable balloons, snakes, and paddles could come with big benefits, too. Flexible
wave energy converters, also known as flexWECs, can harness and convert waves into
usable energy throughout their entire structure. So, no matter where or how wave energy
interacts with a device’s structure, energy converters will be there to transform
that wave into power.
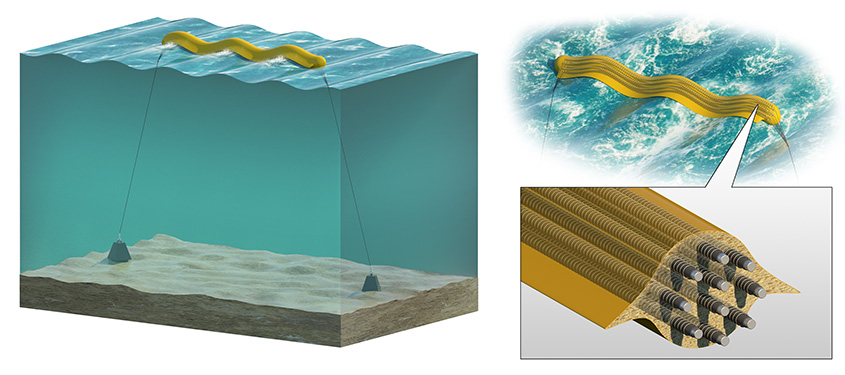
numerous shapes, like snakes and balloons, to capture energy from a wide range of
ocean environments. Illustrations by Besiki Kazaishvili, NREL
Because flexWECs do not concentrate ocean wave energy into a singular energy converter
(like a lone rotary generator or hydraulic piston cylinder) or one power transmission
system (like a drive shaft or gearbox), they avoid accumulating ocean wave forces
that could potentially shut off or damage the machine. Indeed, other wave energy converters
often use large steel frames to protect their rigid bodies from oceanic forces, but
those frames can be expensive and heavy. Instead, flexWECs can go with the flow.
FlexWECs’ frames could also enable them to harness energy from a far wider range of
ocean locations and wave energy frequencies. “One day, there could be DEEC-Tec-based
marine renewable energy farms off the coast of California, Oregon, or Washington,
with these types of wave energy converters potentially powering coastal communities
or the utility grid at large,” Boren said.
High costs are one of the last major hurdles that the blossoming marine energy industry
must overcome to start powering those communities. And DEEC-Tec’s flexible archetypes
could offer an especially cost-effective way to harness wave energy. Because flexWECs
host far more than one energy converter, they could require fewer maintenance trips;
if only a small group of tiny converters requires fixing, all others could continue
operating.
FlexWECs can also be built with more sustainable, cost-effective materials, making
them easier to install and control once out in the ocean. Greater control could mean
increased energy production, allowing operators to adapt to changing ocean conditions
to harness the greatest amount of potential energy.
Because the DEEC-Tec domain is still relatively new, Boren and his team are working
hard to explore exactly how these technologies could create a new generation of marine
energy devices or other energy generating materials. And Boren’s recent patent was
a big push toward a DEEC-Tec future.
“The patent gives further credence as to what DEEC-Tec could become,” Boren said.
“Now, we have a patented foundation to further develop and promote DEEC-Tec both within
NREL and with our external collaborators and industry.”
Learn more about NREL’s Distributed Embedded Energy Converter Technologies. And subscribe to the NREL water power newsletter, The Current, to make sure you don’t miss a water power update.








Gloss